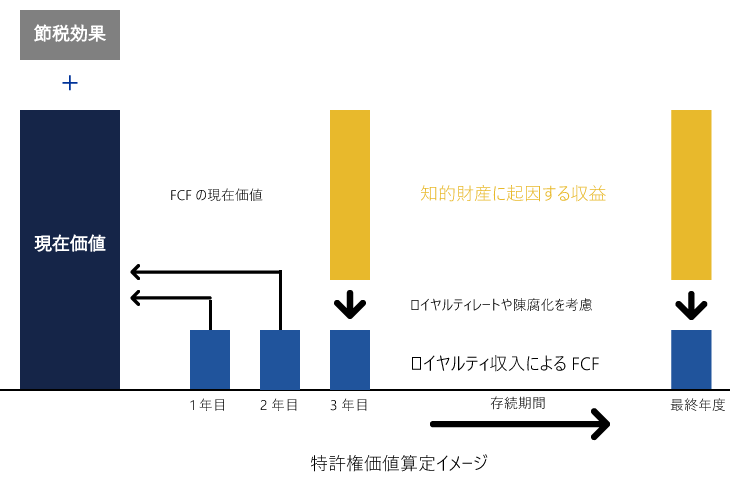
ロイヤルティ免除法における特許権価値の算定は、「ロイヤルティ収入の割引現在価値」、「節税効果(TAB:Tax Amortization Benefit)」の構成要素からなる。
ロイヤリティ免除法 / The Relief from Royalty Method
特許権を対象に、インカムアプローチの中でも特に代表的な手法であるロイヤルティ免除法について紹介します。
ロイヤリティ収入の割引現在価値
ロイヤルティ収入による割引現在価値は、特許権の残存有効期間におけるロイヤルティ収入(Free Cash Flow:FCF)に陳腐化を考慮し、無形資産固有の割引率で割り戻した現在価値として算定される。ここで、FCFは下記算式に示す通り、売上高にロイヤルティレートを乗じ、特許権維持管理費などを控除することにより、特許権保有にかかるキャッシュフローを見積もる。
まず、売上高およびロイヤルティレートの積により、評価の対象となる特許権にかかるロイヤルティ収入となる。しかし、特許権などの技術資産は、代替技術などの台頭により価値が目減りすることが一般的であるため、製品ライフサイクルなどから陳腐化を合理的に見積もる必要が考えらえる。
つぎに、特許権にかかるFCFを現在価値に割り引いた合計が特許権価値となる。参考までに特許権価値評価のイメージを以下に示す。
FCF = 売上高 × ロイヤルティレート × 陳腐化考慮
- 特許権維持管理費 - 法人税等
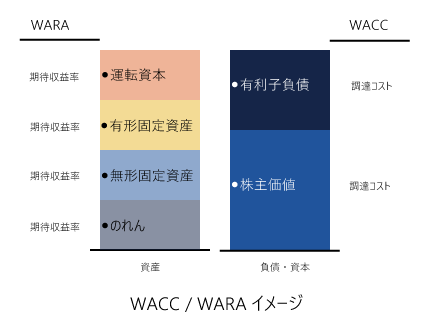
WACCとWARAの関係
特許権にかかる割引率は、資金調達コストの加重平均である加重平均資本コスト(Weighted Average Cost of Capital:WACC)および資金期待収益率の加重平均である加重平均資産コスト(Weighted Average Return on Assets:WARA)と各資産の相対的リスクのバランスを図り、かつ各資産ごとに資本構成を考慮しながら決定する。WARAは運転資本、有形固定資産、無形固定資産、のれん(人的資産も構成)の各資産グループの期待収益率の加重平均であるが、一般的には以下のようになる。
運転資本 < 有形固定資産 < 無形固定資産 < のれん
WACC/WARAイメージ
節税効果
特許権の償却費は税務上の耐用年数のもと損金算入されるため、節税メリットを享受できる。そこで、当該節税効果を価値評価に織り込むため、償却費に税率を乗じた影響額を割引いて現在価値を算定する場合がある。しかし、当該影響によって対象期間におけるFCFが変動し、償却費の計算原資である特許権の現在価値も併せて変動する循環計算となる。そこで、節税効果にかかる現価係数(Discount factor)の期間合計および節税効果考慮後の特許権価値から、節税効果にかかる現在価値が算定されると仮定した場合、以下算定式により特許権価値を評価することになる。
特許権価値 - 特許権価値 × 節税効果にかかる現価係数の期間合計
= ロイヤルティ収入による割引現在価値
特許権価値評価イメージ
Patent Valuation Advisory is a professional firm that specializes in evaluating intellectual property such as patent rights.